TSA Prediction Market: Part 1 - Web Scraping

Overview
Introduction
This is a 5 part series on building a trading bot for next week’s TSA traffic market on Kalshi. We will be covering the following:
-
Part 1: Web scraping to get historical data from the TSA site (Current page)
What is Kalshi?
Kalshi is a prediction market platform where users trade contracts based on the likelihood of real-world events. It offers markets in politics, finance, and current events, allowing users to buy and sell contracts to express their views and potentially profit from accurate predictions. We will talk more about how Kalshi works in a later section.
Part 1: Scraping TSA Data
The data
The first thing we need to build any model is data, so let’s create a process to quickly retrieve the historical TSA volume data. The data is updated daily here. This data will be used as the historical source of “truth” for actual TSA traffic. Our model will also leverage newly released data each day to update its predictions.
As you would expect from a government agency, the data is embedded in the page’s html with no easy option to download. So, we will have to build a web scraper. Luckily, this is easy to do with Python.
The web scraper
We could retrieve the html and parse it for the table and convert this to a dataframe, but pandas has done all this work for us. Using the pandas library, we can get this data into a dataframe in a few lines of code.
url = 'https://www.tsa.gov/travel/passenger-volumes'
header = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0'} # TSA website blocks bot traffic unless you include this
r = requests.get(url, headers=header)
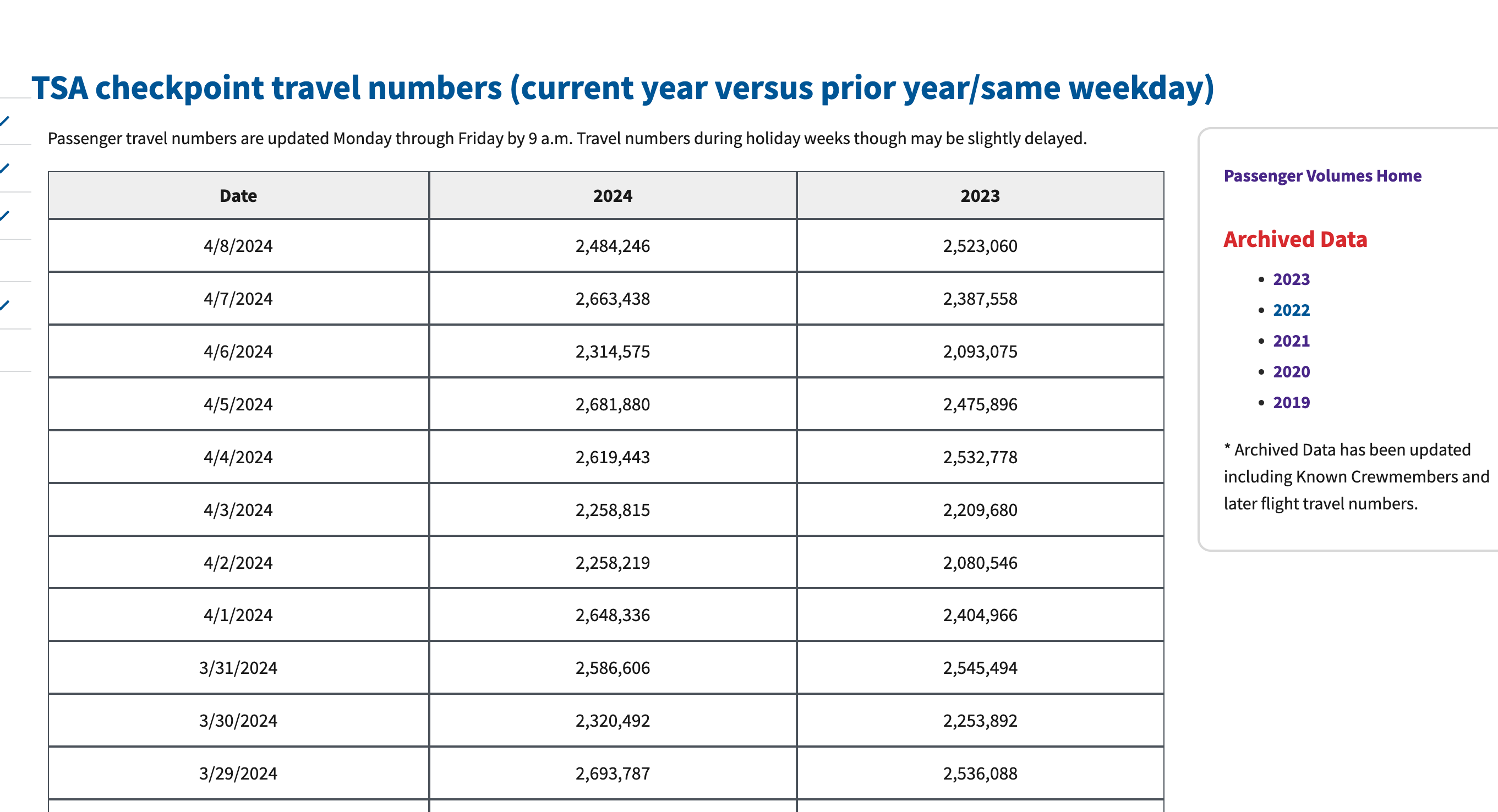
df = pd.read_html(r.text)[0] # Returns a list of dataframes, but we only want one| Date | 2024 | 2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4/8/2024 | 2484246 | 2523060 |
| 1 | 4/7/2024 | 2663438 | 2387558 |
| 2 | 4/6/2024 | 2314575 | 2093075 |
| 3 | 4/5/2024 | 2681880 | 2475896 |
| 4 | 4/4/2024 | 2619443 | 2532778 |
| 5 | 4/3/2024 | 2258815 | 2209680 |
| 6 | 4/2/2024 | 2258219 | 2080546 |
| 7 | 4/1/2024 | 2648336 | 2404966 |
| 8 | 3/31/2024 | 2586606 | 2545494 |
| 9 | 3/30/2024 | 2320492 | 2253892 |
That gets us a pandas dataframe with the current year of data! But, looking again at the TSA page, we can see that they have data going back to 2019 on different pages. Let’s get that data too. Each historical page is structured in a similar format but with the addition of the year appended at the end of the url. Like this…
https://www.tsa.gov/travel/passenger-volumes/2022
Let’s create a function to retrieve any given year of data. The current year of
data has a different url structure which we will need to account for. The below
function create_request_url() takes a one year at a time
as arguments. If the year to process is the current year, it knows to use
the modified url format. Otherwise, it uses the standard url format with
the year appended to the end. We will iterate through the years we care about
calling this function each time.
def create_request_url(year_to_process, current_year):
"""Create Request URL
Creates a URL for fetching TSA data based on the year to process and the current year.
Args:
year_to_process (int): The year for which the data is to be fetched.
current_year (int): The current year.
Returns:
str: The URL for fetching TSA data for the specified year.
"""
base_url = 'https://www.tsa.gov/travel/passenger-volumes'
if year_to_process == current_year:
url = base_url
else:
url = f"{base_url}/{year_to_process}"
return urlNow we have a function that will generate the appropriate request url for any given
year. Next, we will create a function to use this url to actually retrieve the data.
Below we define a function fetch_year_of_tsa_data(). We will call
this function for each year that we iterate through. It then will:
- Call
create_request_url()to define that year’s url - Get the data for that year
- If processing current_year, modified the data format to match the other years.
- Returns the resulting dataframe
def fetch_year_of_tsa_data(year_to_process):
"""Fetch TSA Data for a Specific Year
Fetches TSA (Transportation Security Administration) data for a specific year from the TSA website.
Args:
base_url (str): The base URL of the TSA data website.
year_to_process (int): The year for which the data is to be fetched.
Returns:
pandas.DataFrame: A DataFrame containing the TSA data for the specified year.
"""
header = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0'} # TSA website blocks bot traffic unless you include this
current_year = datetime.datetime.now().year
url = create_request_url(year_to_process, current_year)
logging.warning(f"Processing {year_to_process}")
r = requests.get(url, headers=header)
df = pd.read_html(r.text)[0]
# Structure of current year's data is a bit different
# Here we change the format to match previous years
if year_to_process == current_year:
df = df[['Date', str(current_year)]]
df = df.rename(columns={str(current_year): "Numbers"})
return dfFinally, we need a wrapper function to iterate through
the years calling fetch_year_of_tsa_data() and consolidating
the results.
Here we define a function, fetch_all_tsa_data(). First, we
create an empty list that will hold our dataframe from each
year. Then, we create a for loop to iterate through the years. We know
that TSA data starts at 2019, and we don’t expect that to change. Next,
we pull the data for that year and add that dataframe to our
list of dataframes. Finally, once the final year has been processed,
we union the dataframes together to get the data in a single
dataframe.
def fetch_all_tsa_data():
"""Fetch All TSA Data
Fetches TSA (Transportation Security Administration) data for all available years
up to the current year and merges them into a single DataFrame.
Returns:
pandas.DataFrame: A DataFrame containing all the TSA data for the available years.
"""
dfs = []
for year_to_process in range(2019, datetime.datetime.now().year+1):
df = fetch_year_of_tsa_data(year_to_process)
dfs.append(df)
time.sleep(1) # Wait in between requests to avoid missing years
df_merged = pd.concat(dfs, ignore_index=True, sort=False)
return df_mergedFrom here, we can save the dataframe as a csv to later usage.
Conclusion
In the first part of this series, we discussed the overall goal of creating a TSA traffic prediction model to (hopefully) make money on binary contract markets. We successfully built a webscraper to collect new data from the TSA website every day.
In upcoming posts, we will enhance the model with supplementary data, discuss evaluation methods, and put the model to the test by setting up a live trading bot.
Ways to improve this code
If you want to follow along and add some extra functionality, here are a few areas to expand on:
Additional logging functionality
In any live system, logging can make debugging more efficient. You could expand on the logging in the code examples and save the files for later analysis
Error handling
The above code does not implement any error handling. This leaves it susceptible to breaking down from small changes in inputs or external formatting changes. Error handling would make the webscraper more robust
Data quality checks
We did not implement any data quality checks as part of this process. If the TSA changes the format of their site, we could start reading in incorrect data and we wouldn’t know unless it broke something downstream.